Tourism in India is a vital economic driver, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP, employment, and cultural exchange. The sector’s evolution, bolstered by government initiatives, reflects India’s diverse heritage and the growing importance of sustainable and responsible tourism practices.
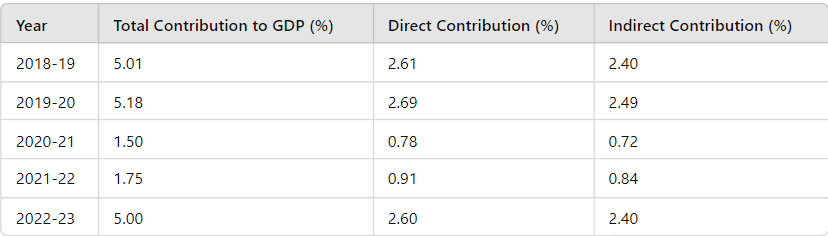
Facts About Tourism’s Contribution to GDP (2018-19 to 2022-23)
Government Initiatives to Boost Tourism
- Infrastructure Development:
- Swadesh Darshan and PRASHAD schemes for creating tourism-related infrastructure.
- Swadesh Darshan 2.0 (SD2.0) promotes sustainable and destination-centric tourism.
- Promotion and Publicity:
- Domestic campaigns like Dekho Apna Desh encourage citizens to explore India.
- Thematic tourism initiatives promote niche areas like wellness, culinary, rural, and eco-tourism.
- Ease of Travel:
- Simplified visa regime with e-Visas for 167 countries.
- Enhanced air connectivity through 53 operational tourism routes under RCS-UDAN.
- Skill Development:
- Programs like Incredible India Tourist Facilitator Certification and Capacity Building for Service Providers improve service standards and create local employment.
- Initiatives like Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi empower local communities with tourism-related training.
Vision for Tourism in India
- Ambitious Goals for 2047:
- Targeting a $1 trillion tourism economy.
- Attracting 100 million international visitors annually.
- Job Creation:
- The sector currently supports 40 million jobs, contributing 7.7% of total employment.
- Investment in tourism creates 78 jobs per ₹1 lakh, compared to only 18 in manufacturing.
- Policy Support:
- 100% FDI allowed under the automatic route in the tourism and hospitality sector.
- Initiatives like Adopt a Heritage: Apni Dharohar, Apni Pehchaan enhance heritage preservation and community involvement.
Tourism’s Impact
1. Indirect Benefits
- Local Industry Support: Boosts sectors like handicrafts, textiles, and transportation.
- Women Empowerment:
- Women-led initiatives in rural tourism, crafts, and culinary arts foster inclusivity.
- Soft Diplomacy: Enhances India’s global image through Track-8 diplomacy and cultural exchange.
- Regional Development: Decentralized tourism drives trickle-down benefits in underdeveloped regions.
2. Globalization’s Role in Tourism
- Positive Impacts:
- 🌍 Cultural Exchange: Promotes India’s heritage globally.
- 📈 Economic Growth: Foreign exchange earnings strengthen the economy.
- ✈️ Connectivity: Better air and rail networks boost both domestic and international travel.
- Negative Impacts:
- 🌿 Environmental Concerns: Over-tourism harms ecosystems and heritage sites.
- 🏙️ Urban Pressure: Overcrowding stresses urban infrastructure.
- 🎭 Cultural Erosion: Excessive commercialization may dilute cultural heritage.
Significance of Tourism
- Cultural Integration: Promotes India’s heritage through handicrafts and historical landmarks.
- Heritage Conservation: Focuses on protecting India’s unique cultural and architectural legacy.
- Multiplier Effect: The sector generates ripple effects across the economy, impacting infrastructure, hospitality, and local businesses.
Challenges in Tourism Development
- Pandemic Aftermath:
- Financial stress from COVID-19 led to a K-shaped recovery in tourism.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor connectivity to remote areas hinders accessibility.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: Lack of adequately trained workers in tourism services.
- Heritage Protection: Inadequate measures to safeguard monuments and sites.
- Unsustainable Tourism: Environmental issues like pollution from excessive plastic usage.
The Road Ahead
India’s tourism sector has immense potential to emerge as a global leader. By addressing infrastructure challenges, promoting sustainable practices, and empowering local communities, the government’s vision for a $1 trillion tourism economy by 2047 can be realized. Tourism not only drives economic growth but also nurtures India’s rich heritage, creating a harmonious blend of development and cultural preservation.